Company - HARBEC
Industry - Manufacturing Contractor
Printer Model - MfgPro230 xS
Printing Technology - Selective Laser Sintering (SLS)
Material - sPro12w
“The XYZprinting's MfgPro230 xS has the capabilities to create any of the plastic end-of-arm tools to operate the robots at HARBEC.” President of HARBEC, Bob Bechtold
BACKGROUND
HARBEC is a manufacturing contractor that has been providing effective solutions to its customers’ problems and requests for more than 40 years. HARBEC provides tight tolerance prototypes, tooling, machined components, and injection-molded parts while prioritizing environmental sustainability. HARBEC has a reputation for exceeding customer expectations by proficiently employing cutting-edge technology to accomplish their objectives.
CHALLENGE
HARBEC uses robots to perform some of the daily manufacturing tasks at its facility. These robots require fitted tools, called end-of-arm tools, to complete their various tasks. Many of these tools require multiple pneumatically actioned claws or grippers attached to a specifically designed bracket.
HARBEC owns many different 3D printing technologies that they can use to create the brackets for each job. Initially, they used a stereolithography (SLA) printer to create brackets. These had decent mechanical properties and worked well, but HARBEC wanted to reduce their weight. Using SOLIDWORKS topology optimization technologies, the HARBEC team created a new design to minimize the part’s weight while meeting its functional requirements. They grew this optimized part in an SLA printer, but the resulting component wasn’t as rigid as they had hoped. They sought a solution that would maintain the lightweight design while recreating the stiffness of the initial part.
SOLUTION
When trials with the SLA printer proved unsuccessful, the HARBEC team considered alternatives, including fused deposition modeling (FDM), Polyjet, and selective laser sintering (SLS). Because these end-of-arm tools require parts that are lightweight, stiff, and dimensionally accurate, HARBEC decided to use the XYZprinting MfgPro230 xS SLS machine with nylon material. The resulting mechanical properties were exactly what they needed. A short inspection revealed that the newly created part had lost a significant amount of weight while keeping a stiffness consistent with the original, non-optimized part.
Below are a few examples of different routes the HARBEC team took as they worked to perfect
this tool.

Material
Accura 25
Mass
100 g
Properties
Ultimate Tensile Strength (UTS) = 38 MPa
Young’s Modulus (YM) = 1590–1660 MPa
Results
Heavy, rigid, high yield strength
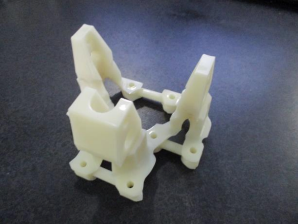
Material
Accura 25
Mass
60 g
Properties
UTS = 38 MPa
YM = 1590–1660 MPa
Results
Lightweight, flexible, low yield strength
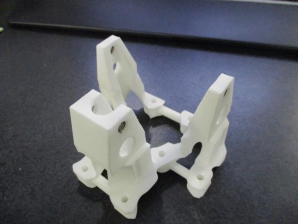
Material
PA 12 (XYZprinting)
Mass
50 g
Properties
UTS = 48 MPa
YM = 1700–1800 MPa
Results
Lightweight, rigid, moderate yield strength
Notably, the PA 12 nylon material has larger values than Accura 25 for many important mechanical properties, which may have enabled the increased rigidity achieved with the polyamide material in the MfgPro230 xS. The XYZprinting MfgPro230 xS uses this material well while maintaining directional accuracy, allowing the team to design a lightweight, rigid, and accurate end-of-arm tool. The tool, fitted with the gripper mechanisms, is pictured below.

RESULTS
The XYZprinting’s MfgPro230 xS can be used to create any of the plastic end-of-arm tools for HARBEC’s robots, meeting their expectations for dimensional accuracy while providing exceptional material properties for optimal tool design. HARBEC is looking forward to exploring more opportunities to improve its manufacturing processes with the XYZprinting MfgPro230 xS.
Topics: Case Study, SLS

 Older
Older